Fiber Cement Siding Cost A Comprehensive Guide

Fiber cement siding cost is a key consideration for any homeowner looking to upgrade their exterior. This guide breaks down the various factors influencing the price, from material selection and labor costs to regional variations and potential cost-saving strategies. We’ll explore different brands, compare fiber cement to other siding options, and help you navigate the often-complex process of budgeting for your project.
Understanding the total cost involves more than just the price per square foot of the siding itself. It’s crucial to factor in installation labor, permits, waste disposal, and potential unexpected expenses. We’ll provide a detailed breakdown of these costs and offer practical advice to help you stay within budget.
Understanding Fiber Cement Siding Costs
Fiber cement siding offers a durable and attractive exterior cladding option for homes, but its cost can vary significantly. Understanding the factors that influence pricing is crucial for accurate budgeting and informed decision-making. This section will break down the components of fiber cement siding costs, helping you navigate the process of choosing the right product for your needs.
Factors Influencing Fiber Cement Siding Prices
Several key factors contribute to the overall cost of fiber cement siding. These include the type of siding (e.g., panels, shingles, shakes), the thickness of the material, the chosen manufacturer and their brand reputation, the complexity of the installation (e.g., intricate trim work, difficult angles), and regional variations in labor rates and material availability. Additionally, the size of your house directly impacts the total square footage requiring coverage, significantly influencing the final cost. Premium features, such as unique colors or textures, also tend to command higher prices.
Material Costs versus Labor Costs
The total cost of a fiber cement siding project is typically divided between material costs and labor costs. Material costs account for the purchase price of the siding itself, including any necessary trim pieces or accessories. Labor costs, on the other hand, cover the wages of the installers, their expertise, and the time required for the installation process. A typical breakdown might see materials accounting for 40-60% of the total cost, with labor representing the remaining portion. The exact proportions depend heavily on the project’s complexity and location. For example, a simple installation on a smaller home with readily available materials might skew more towards material costs, whereas a complex project on a large, multi-story house with difficult angles and requiring specialized labor will likely see a higher proportion of labor costs.
Price Variations Based on Siding Thickness and Manufacturer
Fiber cement siding comes in various thicknesses, typically ranging from 5/16″ to 1/2″. Thicker siding generally offers greater durability and impact resistance, but it also commands a higher price per square foot. Different manufacturers also offer varying price points, reflecting differences in production methods, material quality, and brand recognition. Established, well-known brands often have higher prices than lesser-known manufacturers. For example, James Hardie, a leading brand, tends to be at the higher end of the price spectrum compared to other brands. This difference reflects the brand’s reputation for quality and the associated research and development costs.
Cost Comparison of Different Fiber Cement Siding Brands
The following table provides a general comparison of prices for different fiber cement siding brands. Remember that these are estimates and actual prices can vary based on location, project specifics, and current market conditions. It’s crucial to obtain multiple quotes from local contractors for the most accurate pricing.
| Brand | Price per Square Foot (Estimate) | Features | Warranty |
|---|---|---|---|
| James Hardie | $3.50 – $6.00 | Variety of styles, colors, and textures; high durability and resistance to damage. | 30-year or 50-year warranty depending on the product. |
| CertainTeed | $3.00 – $5.00 | Wide range of styles and colors; good durability and moisture resistance. | 30-year warranty. |
| Nichiha | $4.00 – $6.50 | Known for innovative designs and high-end aesthetics; excellent durability. | 50-year warranty. |
| Allura | $2.50 – $4.50 | Offers a range of styles at a more budget-friendly price point. | 30-year warranty. |
Factors Affecting Total Project Cost
Getting fiber cement siding installed is more than just picking a color; several factors significantly influence the final cost. Understanding these variables helps you budget accurately and avoid unpleasant surprises during the project. This section breaks down the key elements that impact your overall expenditure.
House size and complexity directly correlate with the amount of material and labor needed. Larger homes, naturally, require more siding, leading to higher material costs. Similarly, complex house designs with many angles, dormers, or intricate details increase both material and labor costs as installers require more time and precision. For example, a simple ranch-style home will cost considerably less than a Victorian with multiple gables and turrets. The increased labor intensity translates to a higher hourly rate for the installation crew.
Installation Costs Beyond Material
Beyond the cost of the fiber cement siding itself, several additional expenses contribute to the total project cost. These often-overlooked items can significantly inflate the final bill if not properly accounted for.
Permits are necessary in most jurisdictions before any exterior work begins. The permit fees vary widely depending on location and the scope of the project. Waste removal is another critical cost. Removing old siding, debris, and packaging materials generates a substantial amount of waste. Disposing of this responsibly, either through your local waste management service or a specialized contractor, adds to the overall expense. These costs can range from a few hundred dollars to well over a thousand depending on project size and local regulations.
Preparation Work Costs
Preparing the house for new siding is a crucial step that often impacts the total cost. If you have existing siding, its removal is a significant undertaking. The cost depends on the type of siding being removed (e.g., wood, vinyl, aluminum), its condition (difficult-to-remove materials increase labor), and the overall square footage. Furthermore, any necessary repairs to the underlying sheathing or structure will add to the expenses. In some cases, this preparatory work can cost as much as, or even more than, the siding itself, especially if extensive repairs are required.
Unexpected Expenses
It’s wise to anticipate unforeseen costs when undertaking any home renovation project. These unexpected expenses can quickly derail your budget if not planned for.
- Unforeseen Repairs: Discovering rotted wood or damaged sheathing during siding removal can necessitate costly repairs.
- Material Shortages: Delays due to supply chain issues or unexpected material needs can lead to increased costs and project timelines.
- Additional Labor: Complex installations or unforeseen challenges may require extra labor hours.
- Changes to the Scope of Work: Mid-project design changes or additions will inevitably add to the expense.
- Site Conditions: Unexpected obstacles like difficult terrain or the need for specialized equipment can increase costs.
Comparing Fiber Cement to Other Siding Materials
Choosing the right siding for your home involves weighing initial cost against long-term expenses. While fiber cement offers durability and longevity, it’s essential to compare it to other popular options like vinyl, wood, and aluminum to make an informed decision. This section will discuss the cost differences and long-term implications of each material.
Fiber cement’s higher upfront cost is often offset by its superior lifespan and reduced maintenance needs compared to other materials. Let’s delve into a more detailed comparison.
Cost Comparison of Siding Materials
The initial cost of siding varies significantly depending on the material, labor costs, and regional factors. Generally, vinyl siding is the least expensive upfront, followed by aluminum, wood, and then fiber cement. However, these initial cost differences can be misleading when considering the overall lifetime cost. For instance, a cheaper vinyl siding installation might require replacement sooner than a more expensive fiber cement installation, ultimately leading to higher overall costs over the building’s lifespan.
Long-Term Cost Benefits and Drawbacks
Vinyl Siding: Vinyl is inexpensive upfront, but its relatively short lifespan (15-20 years) and susceptibility to damage from strong impacts or extreme weather necessitate more frequent replacements, increasing long-term costs. While low maintenance, repairs can be costly if significant damage occurs.
Wood Siding: Wood siding offers a classic aesthetic, but it demands considerable maintenance. Regular painting or staining, along with potential repairs for rot, insect damage, or warping, can significantly increase long-term costs. Its lifespan can vary greatly depending on the wood type and maintenance, ranging from 20-50 years.
Aluminum Siding: Aluminum siding is durable and low-maintenance, resisting rot and insect damage. However, it’s prone to denting and can be susceptible to hail damage. Its lifespan is generally longer than vinyl, around 30-40 years, but still shorter than fiber cement.
Fiber Cement Siding: Fiber cement boasts a significantly longer lifespan (50 years or more) and superior resistance to fire, insects, rot, and extreme weather. While the initial cost is higher, its long lifespan and low maintenance requirements result in lower overall long-term costs. Repairs are typically less frequent and less expensive compared to other materials.
Siding Material Comparison Table
| Siding Material | Lifespan (Years) | Maintenance Requirements | Approximate Overall Cost (per sq ft – estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | 15-20 | Low; occasional cleaning | $3-$7 |
| Wood | 20-50 | High; regular painting/staining, potential repairs | $8-$15 |
| Aluminum | 30-40 | Low; occasional cleaning, potential repairs | $6-$12 |
| Fiber Cement | 50+ | Low; occasional cleaning, infrequent repairs | $10-$20 |
Note: The cost estimates provided in the table are approximations and can vary significantly based on factors such as material quality, labor costs, regional differences, and project complexity. It’s crucial to obtain multiple quotes from reputable contractors for accurate pricing in your specific area.
Cost-Saving Strategies for Fiber Cement Siding

Source: imimg.com
Choosing fiber cement siding can significantly enhance your home’s curb appeal and longevity, but the initial cost can be substantial. Fortunately, several strategies can help you minimize expenses without sacrificing quality. This section provides practical approaches to keep your fiber cement siding project within budget.
Minimizing Labor Costs During Installation, Fiber cement siding cost
Labor costs often represent a significant portion of the total project expense. Careful planning and selection of installation methods can significantly reduce this burden. Opting for simpler designs, as discussed later, inherently reduces installation time. Additionally, pre-planning your project meticulously, including precise measurements and material ordering, minimizes on-site adjustments and delays, which translates directly to lower labor charges. Consider engaging a contractor who employs efficient installation techniques and utilizes tools that speed up the process, such as specialized cutting equipment for fiber cement boards. Getting multiple quotes and comparing labor rates is crucial; don’t hesitate to ask contractors about their experience with fiber cement and their typical installation timelines.
Negotiating Prices with Contractors
Negotiating with contractors is an essential part of controlling costs. Begin by obtaining detailed, itemized quotes from multiple contractors. This allows for direct comparison of pricing and services. Clearly articulate your budget upfront and be prepared to discuss potential trade-offs. For example, you might be willing to compromise on minor details (like a less expensive trim option) to stay within your budget. Remember to emphasize the importance of quality workmanship and materials; this assures the contractor that you’re not solely focused on the lowest price. Negotiating may involve exploring payment schedules or securing discounts for paying in full upfront. Don’t be afraid to walk away if a deal doesn’t feel right; there are always other contractors available.
Potential Savings with DIY Installation
DIY installation offers the potential for substantial cost savings, but it’s crucial to realistically assess your skills and comfort level. Fiber cement siding is not a beginner’s project; it requires precision cutting, proper fastening, and an understanding of building codes. Improper installation can lead to damage, leaks, and costly repairs down the line. If you lack experience, the risks of costly mistakes outweigh the potential savings. If you decide to proceed with DIY installation, invest in high-quality tools and take the time to thoroughly research proper installation techniques. Safety is paramount; wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including eye protection, gloves, and a dust mask, throughout the entire process. Consider taking a hands-on workshop or watching detailed instructional videos before starting.
Reducing Costs with Simpler Siding Designs
Complex siding designs, featuring intricate patterns, multiple layers, or extensive trim work, significantly increase both material and labor costs. Choosing a simpler, more streamlined design can lead to substantial savings. A clean, classic look often requires less material and is quicker to install, resulting in lower overall expenses. While you might sacrifice some visual flair, the cost savings can be significant. For example, opting for large, uniform panels instead of smaller, more detailed pieces reduces installation time and material waste. Similarly, minimizing the use of decorative trim pieces can lead to notable cost reductions. Before finalizing your design, consider consulting with a design professional to explore cost-effective alternatives that still meet your aesthetic preferences.
Visual Representation of Cost Breakdown

Source: legacyusa.com
Understanding the cost of a fiber cement siding project requires visualizing how different elements contribute to the final price. A clear breakdown helps homeowners budget effectively and negotiate fairly with contractors. The following description is an article illustrating a typical cost distribution.
A pie chart visually represents the cost breakdown, using different colors to represent each component. The largest slice, perhaps 40-50%, would be in a deep blue and labeled “Materials.” This includes the cost of the fiber cement siding itself, along with necessary underlayment, flashing, and fasteners. A slightly smaller slice, maybe 25-35%, shown in a vibrant green, would represent “Labor.” This encompasses the cost of skilled labor for installation, including preparation, installation of the siding, and cleanup. A smaller orange slice, approximately 10-15%, represents “Permits and Inspections.” This covers all government-mandated permits and inspection fees required for the project. A smaller, light purple slice, around 5-10%, shows “Waste Removal and Disposal.” This section covers the costs associated with removing old siding, debris disposal, and responsible waste management. Finally, a small, dark grey slice, approximately 5-10%, represents “Contingency/Unexpected Costs.” This accounts for unforeseen issues, such as hidden damage or material shortages, providing a buffer for potential extra expenses. The percentages are approximate and will vary depending on project specifics, location, and contractor. For example, a more complex project with extensive removal of old siding might have a larger “Waste Removal and Disposal” slice, while a project in an area with low permit fees would have a smaller “Permits and Inspections” slice.
Cost Component Details
The pie chart provides a high-level overview. A more detailed breakdown could include specific costs within each category. For instance, under “Materials,” one could list the cost per square foot of the fiber cement siding, the cost of underlayment, and the cost of fasteners separately. Similarly, “Labor” could be broken down into the hourly rate of the installers and the total number of labor hours estimated for the project. This granular level of detail would help homeowners understand the reasoning behind the overall cost estimate and make informed decisions.
Regional Cost Variations
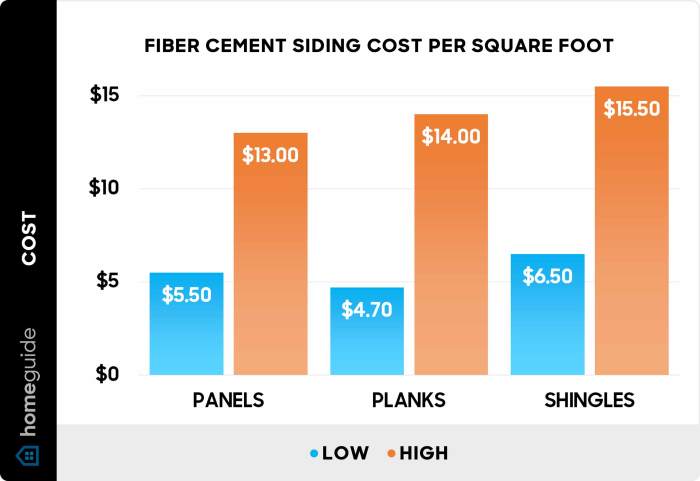
Source: homeguide.com
Fiber cement siding costs aren’t uniform across the country. Several factors, primarily related to labor and material availability, create significant regional price differences. These variations can impact both the cost of the siding itself and the cost of installation. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate budgeting and realistic project planning.
The price of fiber cement siding, like many building materials, fluctuates based on regional supply and demand. Areas with a high concentration of construction projects or limited access to manufacturing facilities may experience higher material costs. Similarly, labor costs, which significantly contribute to the overall project expense, vary widely depending on location. High-cost-of-living areas generally have higher labor rates, impacting the final installation price. Transportation costs also play a role; shipping materials long distances increases the overall cost.
Labor Costs and Material Availability Influence on Regional Pricing
Labor costs are a major component of the total fiber cement siding project cost. Regions with higher minimum wages or strong union presence will naturally see higher labor rates. The availability of skilled installers also impacts the price; areas with a shortage of experienced installers may command higher fees due to increased demand. Material availability also influences costs. Regions with limited access to fiber cement siding manufacturers or distribution centers may experience higher prices due to increased transportation costs and potentially lower competition. For example, a remote rural area might have significantly higher costs compared to a large metropolitan area with multiple suppliers and a large pool of installers.
Examples of Price Differences Across Various Regions
While precise pricing varies greatly based on specific project details (house size, complexity of installation, etc.), we can illustrate regional differences. For instance, a project in New York City might cost significantly more than a comparable project in a smaller city in the Midwest. This difference reflects higher labor costs and potentially higher material transportation expenses in the denser urban environment of New York City. Conversely, areas in the South, known for lower labor costs, might see lower overall project costs. The West Coast, depending on the specific location, may experience fluctuating prices due to factors such as transportation costs and proximity to manufacturing plants.
Visual Representation of Regional Cost Ranges
Imagine a map of the United States color-coded to represent fiber cement siding installation cost ranges. The color gradient would range from a light green (representing the lowest cost regions) to a deep red (representing the highest cost regions). States with significant metropolitan areas and high labor costs, such as California, New York, and parts of the Northeast, would likely be represented in darker shades of red. Conversely, states with lower labor costs and potentially greater access to manufacturing facilities, such as parts of the South and Midwest, would likely be depicted in lighter shades of green. The map would include a legend clearly defining the cost ranges associated with each color, perhaps broken down into tiers like “$10-$15 per square foot,” “$15-$20 per square foot,” and “$20+ per square foot.” This visual aid provides a quick understanding of the broad regional cost variations across the nation. It’s crucial to remember that these are broad ranges and actual costs would depend on many factors unique to each project.
Outcome Summary
Ultimately, the cost of fiber cement siding is a balance between upfront investment and long-term value. While it may be more expensive initially than some alternatives like vinyl, its durability, low maintenance, and aesthetic appeal often translate to significant savings over the lifespan of your home. By carefully considering the factors outlined in this guide, you can make an informed decision that best suits your needs and budget.
Questions and Answers
What is the average lifespan of fiber cement siding?
Fiber cement siding typically lasts 50 years or more with proper maintenance.
Can I install fiber cement siding myself?
While DIY is possible, it’s challenging and requires significant experience. Professional installation is generally recommended for optimal results and safety.
Does fiber cement siding require regular painting?
No, fiber cement siding is naturally resistant to rot, insects, and fire. While it can be painted for aesthetic reasons, it doesn’t require regular repainting.
How does climate affect fiber cement siding cost?
Extreme weather conditions can impact installation costs and may necessitate additional protective measures, potentially increasing the overall price.
What are some common warranty terms for fiber cement siding?
Warranties vary by manufacturer but often cover defects in materials and workmanship for a significant period, typically 25-50 years.
Comments are closed.