House Siding Types A Homeowners Guide

House siding types are far more diverse than you might think! Choosing the right siding for your home isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s a crucial decision impacting durability, maintenance, energy efficiency, and even your home’s resale value. This guide explores the popular options – from classic wood to modern metal – helping you weigh the pros and cons to find the perfect fit for your style and budget. We’ll cover everything from installation tips to long-term maintenance, ensuring you’re well-equipped to make an informed choice.
Consider your climate – a material ideal for a desert might not fare well in a humid coastal environment. Budget is another key factor; some materials are significantly pricier upfront but may save you money in the long run through lower maintenance. Finally, don’t forget aesthetics! Your siding should complement your home’s architectural style and your taste, creating a cohesive and visually appealing exterior.
Introduction to House Siding
House siding is the outer covering of a house’s exterior walls. It serves several crucial purposes, protecting your home from the elements, providing insulation, and enhancing its aesthetic appeal. Choosing the right siding is a significant decision impacting both the longevity and curb appeal of your property. Many factors need consideration before making a selection.
Choosing the right siding involves careful consideration of several key factors. Climate plays a significant role; areas with harsh winters might benefit from materials with superior insulation and weather resistance, while those with intense sun exposure require siding that can withstand fading and heat damage. Budget is another critical factor, as siding materials range widely in price. Finally, aesthetics are important; siding should complement the architectural style of the house and the homeowner’s personal preferences.
Factors Influencing Siding Choices
The ideal siding material is determined by a careful balancing act between budget, climate, and aesthetic goals. For example, a homeowner in a coastal area prone to high winds and salt spray would prioritize durability and weather resistance over a less expensive but less resilient option. Similarly, someone on a tight budget might opt for vinyl siding, while a homeowner seeking a more upscale look might choose fiber cement or wood. Ultimately, the best choice reflects the homeowner’s priorities and resources.
Architectural Styles and Typical Siding Materials
Different architectural styles often lend themselves to particular siding materials. For instance, a traditional Victorian home might be clad in wood clapboard, creating a classic and elegant look. A contemporary, minimalist home might utilize sleek metal panels for a modern and clean aesthetic. A rustic farmhouse style might feature board and batten siding for a charming and cozy appearance. The choice of siding material can significantly impact the overall feel and character of the home. A Craftsman style bungalow, with its emphasis on natural materials and handcrafted details, often utilizes wood shingles or stucco. Conversely, a sleek, mid-century modern home might be clad in aluminum siding or large format fiber cement panels. The connection between architectural style and siding is a crucial aspect of home design.
Common Siding Materials
Choosing the right siding for your house is a big decision, impacting both aesthetics and long-term costs. Several materials offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, making it crucial to understand their properties before making a choice. This section will delve into the characteristics of some of the most common siding materials available.
Wood Siding
Wood siding offers a classic, natural look that many homeowners find appealing. Several types exist, including clapboard (overlapping horizontal boards), shiplap (butted boards), and shingles (individual pieces). However, wood requires significant maintenance. It’s susceptible to rot, insect infestation, and damage from moisture. Regular painting or staining is essential to protect it from the elements, adding to the overall cost of ownership. The initial cost of wood siding can vary greatly depending on the type of wood used (e.g., cedar, redwood) and the quality of the installation. High-end wood siding can be quite expensive, while less expensive options may require more frequent maintenance.
Vinyl Siding vs. Fiber Cement Siding
Vinyl and fiber cement are popular alternatives to wood, offering different strengths and weaknesses. Vinyl siding is relatively inexpensive and easy to install, requiring minimal maintenance. It’s resistant to rot, insects, and moisture. However, it’s not as durable as fiber cement and can be easily damaged by impact. It also tends to fade over time, particularly in areas with intense sunlight. Fiber cement siding, on the other hand, is significantly more durable and resistant to damage, fire, and insects. It also offers a more realistic wood-like appearance than vinyl. However, it’s more expensive than vinyl and requires more careful handling during installation. It’s heavier than vinyl, which can make installation slightly more challenging.
Metal Siding
Metal siding, including aluminum, steel, and zinc options, offers exceptional durability and longevity. It’s highly resistant to fire, insects, and rot, requiring minimal maintenance. Aluminum siding is lightweight and relatively inexpensive, while steel offers greater strength and durability but is more costly. Zinc siding is known for its long lifespan and attractive patina that develops over time. However, metal siding can dent, and its appearance may not appeal to all homeowners. Additionally, metal siding can be noisy during rain or hail storms.
| Siding Type | Lifespan (Years) | Maintenance Requirements | Initial Cost (Relative) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | 20-50 (depending on wood type and maintenance) | High (regular painting/staining, repairs) | Medium to High |
| Vinyl | 20-40 | Low (occasional cleaning) | Low |
| Fiber Cement | 50+ | Medium (periodic cleaning, occasional painting) | Medium to High |
| Metal (Aluminum/Steel/Zinc) | 50+ | Low (occasional cleaning) | Medium to High (Steel more expensive than Aluminum) |
Siding Installation Methods

Source: dreamworxexteriors.com
Getting your new siding installed correctly is crucial for its longevity and the overall look of your home. Different siding materials require different approaches, and proper installation techniques are key to preventing issues like leaks, warping, and premature wear. This section details the processes for installing some of the most popular siding types.
Vinyl Siding Installation
Vinyl siding installation is generally considered a DIY-friendly project for those with basic construction skills. Preparation is key. First, you’ll need to remove the old siding (if applicable), ensuring the underlying sheathing is sound and free from rot or damage. Any necessary repairs should be made before proceeding. Next, install starter strips along the bottom edge of the wall, ensuring they’re level. Vinyl siding is then installed from bottom to top, overlapping each piece according to manufacturer’s instructions. J-channels are used at corners and around windows and doors to create a neat and weathertight finish. Finally, install the finishing pieces, such as the drip edge and J-channels at the top. Remember to leave expansion gaps as specified by the manufacturer to allow for thermal expansion and contraction.
Wood Siding Installation
Installing wood siding requires more precision and carpentry skills than vinyl. Proper flashing and sealing are vital to prevent water damage. Before installation, the wall sheathing should be inspected and any damaged areas repaired. A weather-resistant barrier, such as house wrap, is typically installed over the sheathing. Flashing is then installed around windows, doors, and other penetrations in the wall to divert water away from these vulnerable points. Wood siding is usually installed horizontally or vertically, depending on the style, with each piece carefully overlapped and nailed securely. Caulk is applied to seal gaps between siding boards and around flashing to create a watertight seal. A final coat of sealant or paint protects the wood from the elements.
Fiber Cement and Metal Siding Installation
Fiber cement and metal siding installation share some similarities but also have distinct differences. Both require more specialized tools and often professional installation. Fiber cement boards are cut to size and installed using nails or screws, similar to wood siding. However, fiber cement is heavier and requires more robust fastening. Specialized saws are often needed to cut the boards cleanly and accurately. Metal siding, often made of aluminum or steel, is typically installed using concealed fasteners, which provides a cleaner, more seamless look. Overlapping seams are crucial for preventing leaks. Both fiber cement and metal siding require attention to detail to ensure proper alignment and a professional finish. Specialized tools like panel cutters, snap-lock pliers, and rivet guns may be necessary for metal siding.
Safety Precautions for Siding Installation
Proper safety precautions are paramount regardless of the siding type.
- Always wear appropriate safety gear, including safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection.
- Use a stable ladder or scaffolding and ensure it’s properly secured.
- Be mindful of overhead power lines and avoid contact.
- Use caution when working with sharp tools and power equipment.
- Follow manufacturer’s instructions for handling and installation of siding materials.
- Take breaks to avoid fatigue and maintain focus.
- If you are not comfortable performing the installation yourself, hire a qualified professional.
Siding Maintenance and Repair
Keeping your house siding in good condition is crucial for protecting your home from the elements and maintaining its curb appeal. Regular maintenance prevents small problems from becoming costly repairs, extending the lifespan of your siding and saving you money in the long run. Different siding materials require slightly different care, so understanding your siding type is the first step.
Routine Maintenance for Different Siding Materials
Regular cleaning and inspection are key to preventing significant siding issues. For vinyl siding, a simple power washing once or twice a year, using a low-pressure setting to avoid damage, is usually sufficient. Always inspect for cracks, loose panels, or signs of insect infestation after cleaning. Wood siding requires more attention. Annual cleaning with a soft brush and mild detergent is necessary, followed by a thorough inspection for rot, insect damage, or loose nails. Consider applying a protective sealant every few years to help prevent moisture damage. Fiber cement siding is relatively low-maintenance. Cleaning with a garden hose and a soft brush is typically enough, along with a yearly inspection for cracks or damage. Remember to always check for loose or damaged caulking around windows and doors, regardless of your siding type.
Repairing Minor Damage
Minor damage to siding can often be repaired easily. Small cracks in vinyl siding can sometimes be filled with a vinyl-compatible caulk. For larger cracks or holes, replacing the damaged section is usually necessary. Wood siding repairs often involve replacing damaged boards. Rotted wood needs to be cut out and replaced with new, pressure-treated lumber. Ensure to properly seal any exposed wood edges to prevent future rot. Minor chips or cracks in fiber cement siding can often be filled with a patching compound specifically designed for fiber cement. Always allow sufficient drying time before painting or sealing repaired areas.
Replacing Damaged Sections of Siding
Replacing larger sections of damaged siding requires more effort but is often a manageable DIY project for homeowners with some basic carpentry skills. When selecting replacement materials, match the color and type to the existing siding as closely as possible. For vinyl siding, simply remove the damaged section by carefully prying it loose from the underlying structure, install the new section, and secure it with nails or screws. Replacing wood siding requires more precision, as you’ll need to cut and fit the replacement board to match the existing ones. Ensure proper nailing or screwing to prevent future movement. Fiber cement siding replacement is similar to wood siding; accurate measurements and cuts are crucial for a seamless repair. Always wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves and eye protection, when working with any type of siding.
Common Siding Problems, Causes, and Repair Solutions
| Problem | Cause | Repair Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cracked Vinyl Siding | Impact damage, extreme temperature changes | Replace the damaged section. For minor cracks, use vinyl caulk. | Regular inspection, protect siding from impact. |
| Rotting Wood Siding | Moisture intrusion, insect infestation | Replace the rotted section with pressure-treated lumber. | Regular painting/sealing, proper ventilation. |
| Loose Fiber Cement Siding | Improper installation, wind damage | Re-secure the siding with appropriate fasteners. Replace damaged sections. | Ensure proper installation, regular inspection. |
| Peeling Paint (Wood Siding) | Poor paint quality, lack of maintenance | Scrape off old paint, prime and repaint. | Regular painting, use high-quality paint. |
Siding Styles and Aesthetics: House Siding Types
Choosing the right siding isn’t just about protection; it’s about enhancing your home’s curb appeal and reflecting your style. The style, color, and texture of your siding significantly impact the overall look and feel of your house, influencing how it interacts with its surroundings. Understanding the aesthetic possibilities is key to making a choice that complements your home’s architecture and landscaping.
Different siding patterns and profiles create distinct visual effects. The choice affects not only the visual appeal but also the perceived scale and proportion of your house.
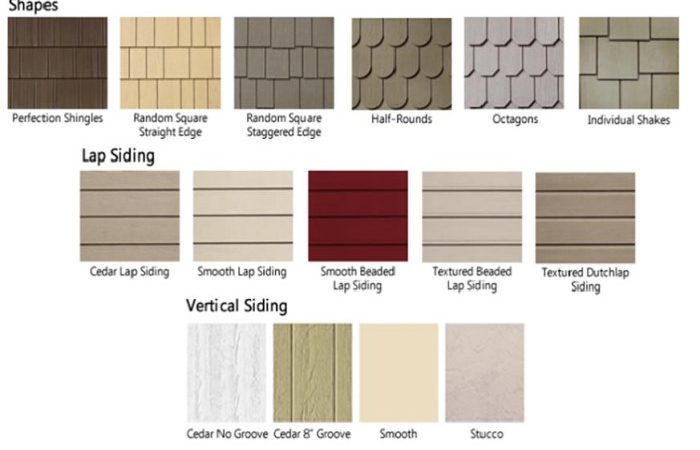
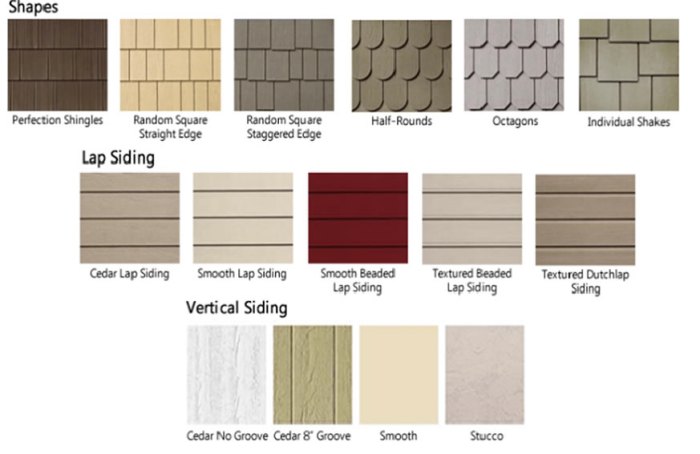
Siding Patterns and Profiles
The most common siding profiles offer a wide range of visual options. Clapboard siding, with its overlapping horizontal boards, creates a classic, traditional look. Shingle siding, often made of wood, asphalt, or fiber cement, provides a more textured, rustic appearance, especially effective on homes with a craftsman or cottage style. Board and batten siding, featuring wide vertical boards with narrow strips of wood (battens) covering the seams, offers a clean, modern, and sometimes farmhouse-style aesthetic. Each profile contributes a unique character to the home’s exterior. For instance, a home with a steep roofline might look better with vertical board and batten siding, emphasizing height, while clapboard siding would suit a more sprawling ranch-style home.
The Visual Impact of Color and Texture
Color plays a crucial role in setting the mood and style of your home. Light colors, such as creams, whites, and pastels, create a sense of spaciousness and airiness, making a home appear larger and brighter. Darker colors, like deep blues, grays, and browns, offer a more dramatic and sophisticated look, adding depth and visual weight. Texture adds another layer of visual interest. Smooth siding offers a clean, contemporary feel, while textured siding, such as that with a wood grain or stucco-like finish, creates a more rustic or traditional look. The interplay of color and texture can significantly influence the overall aesthetic, with certain combinations better suited to specific architectural styles. A Victorian home, for example, might be enhanced by a darker color with a textured finish, while a modern home might benefit from a light color with a smooth finish.
Siding and Architectural Styles
The choice of siding should harmonize with the architectural style of the house. A Colonial-style home might be beautifully complemented by clapboard siding in a muted, traditional color. A Craftsman-style home could benefit from shingle siding in earthy tones. A contemporary home might look best with smooth, fiber cement siding in a sleek, modern color. The siding should enhance the home’s existing features, rather than clashing with them. Consider the details like window trim, rooflines, and overall proportions when making your decision.
The Aesthetic Impact of Contrasting Siding Materials
Using contrasting siding materials on a single home can create a striking and visually interesting effect. Imagine a home with a main body clad in light gray clapboard siding, accented by darker brown board and batten siding around the entryway and window frames. This contrast draws the eye to specific architectural features, creating visual interest and depth. Another example might be using a lighter-colored stone veneer on the lower portion of a home and a darker wood-like siding on the upper portion. Such contrasting elements can highlight architectural details and create a more dynamic and layered appearance. The key is to use the contrast strategically to enhance the home’s features, rather than creating a jarring or chaotic effect. A well-executed contrast can elevate the home’s overall aesthetic, showcasing its unique character and style.
Environmental Considerations
Source: dynastyrestores.com
Choosing house siding involves more than just aesthetics and durability; it significantly impacts the environment. From manufacturing processes to disposal methods, the materials used in your siding have a lifecycle that affects our planet. Understanding this lifecycle helps make informed decisions that minimize your environmental footprint.
Different siding materials have varying environmental impacts. Manufacturing processes consume energy and resources, and some materials release harmful emissions during production. Similarly, disposal methods can contribute to landfill waste. The energy efficiency of the siding itself also plays a crucial role in your home’s overall energy consumption and, consequently, its carbon footprint.
Manufacturing and Disposal Impacts, House siding types
The environmental impact of siding manufacturing varies greatly depending on the material. For example, vinyl siding, while relatively inexpensive, relies heavily on petroleum-based plastics, resulting in significant carbon emissions during production. Wood siding, while a renewable resource, can involve deforestation and transportation impacts if not sourced sustainably. Metal sidings, such as aluminum and steel, have higher upfront energy demands for manufacturing but generally have longer lifespans, reducing the overall environmental impact over time. Finally, fiber cement siding, while durable, often requires energy-intensive manufacturing processes.
Disposal is another crucial factor. Vinyl siding is notoriously difficult to recycle and often ends up in landfills. Wood siding, if not treated with chemicals, is biodegradable, but improper disposal can still lead to environmental issues. Metal siding is recyclable, offering a more environmentally friendly end-of-life option. Proper disposal and recycling programs are vital in minimizing the long-term environmental impact of all siding types.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
The energy efficiency of your siding directly influences your home’s heating and cooling costs. Materials with high R-values (a measure of thermal resistance) help insulate your home, reducing energy consumption. For example, fiber cement siding, with its excellent insulating properties, can contribute to significant energy savings compared to vinyl siding. Similarly, well-insulated wood siding, especially when combined with proper installation techniques, can also improve energy efficiency. Conversely, materials with low R-values, such as certain types of vinyl, may lead to higher energy bills. Choosing energy-efficient siding can result in lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint over the lifespan of your home.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Siding Choices
Several siding options offer more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternatives. Recycled materials are increasingly used in siding production, such as recycled plastic in composite siding. Siding made from rapidly renewable resources, such as bamboo, presents a sustainable choice, though its durability and availability may be limited in some regions. Additionally, sustainably harvested wood siding, certified by organizations like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), ensures responsible forestry practices. Choosing locally sourced materials can also reduce transportation emissions and support local economies. Finally, proper installation is key; reducing waste during installation and choosing installers committed to sustainable practices can significantly improve the environmental performance of your siding choice.
Choosing environmentally responsible siding is a long-term investment that benefits both your wallet and the planet. By considering the manufacturing process, disposal options, and energy efficiency of various materials, you can make a sustainable choice that reduces your home’s environmental impact and contributes to a greener future.
Cost Analysis of Siding Options

Source: dluxeconstruction.com
Choosing the right siding for your home involves careful consideration of aesthetics, durability, and, importantly, cost. The total expense can vary significantly depending on the material selected, the size of your house, and the complexity of the installation. This section breaks down the cost factors to help you make an informed decision.
Average Cost Per Square Foot of Different Siding Materials
Siding material costs vary widely. Prices are influenced by factors like quality, brand reputation, and regional availability. These are average figures and can fluctuate based on current market conditions. Always obtain multiple quotes from reputable contractors to get accurate pricing for your specific project.
| Siding Material | Average Cost per Square Foot (Material Only) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | $1-$5 | Lower-end vinyl can be less expensive but may not be as durable. |
| Fiber Cement | $2-$8 | More expensive upfront, but offers superior durability and longevity. |
| Wood | $3-$15+ | Price varies greatly depending on wood type (e.g., cedar, redwood) and quality. Requires more maintenance. |
| Metal | $3-$10+ | Price depends on the type of metal (e.g., aluminum, steel, zinc) and finish. |
| Brick | $10-$20+ | Typically the most expensive option, offering exceptional durability. |
Factors Influencing Overall Siding Installation Cost
The overall cost of siding installation isn’t solely determined by material prices. Several other factors significantly impact the final bill.
- Labor Costs: Labor constitutes a substantial portion of the total cost. The complexity of the project (e.g., intricate detailing, removal of existing siding) directly affects labor hours and therefore the cost.
- Material Costs: Beyond the siding itself, you’ll need additional materials like flashing, trim, fasteners, and underlayment. These add to the overall material expense.
- Permits and Inspections: Building permits and inspections are mandatory in most areas. The cost of permits varies depending on location and project scope.
- Preparation Work: Before installation, existing siding may need removal, repairs to the underlying structure might be necessary, and surface preparation (cleaning, priming) can add to the expense.
Budgeting for Siding Projects and Finding Cost-Effective Solutions
Careful planning is essential for managing the cost of a siding project.
- Get Multiple Quotes: Obtain at least three detailed quotes from reputable contractors to compare pricing and services.
- Prioritize Needs: Determine which features are essential and which are desirable. Prioritizing needs helps to make cost-effective choices.
- Consider DIY Options (with caution): For those with experience, some aspects of the project might be DIY-friendly, potentially reducing labor costs. However, this approach should only be undertaken if you have the necessary skills and tools to avoid mistakes.
- Explore Financing Options: Home improvement loans or financing options can help spread the cost over time.
Comparative Cost Analysis of Siding Options (Per 1000 sq ft)
This table provides a rough estimate of total costs (material and labor combined) for different siding types, assuming a 1000 square foot area. Remember that actual costs can vary widely depending on your location, contractor, and project specifics.
| Siding Material | Estimated Total Cost (Material & Labor) per 1000 sq ft | Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | $5,000 – $10,000 | $5,000 – $10,000 | Lower end of the range for basic installations. |
| Fiber Cement | $10,000 – $20,000 | $10,000 – $20,000 | Higher upfront cost, but potentially longer lifespan. |
| Wood | $15,000 – $30,000+ | $15,000 – $30,000+ | Significant variation depending on wood type and quality. |
| Metal | $12,000 – $25,000+ | $12,000 – $25,000+ | Cost varies significantly based on metal type and finish. |
| Brick | $20,000 – $40,000+ | $20,000 – $40,000+ | Generally the most expensive option. |
Final Thoughts
Selecting the right house siding is a significant investment, impacting both the beauty and longevity of your home. By carefully considering factors like climate, budget, and aesthetics, and understanding the characteristics of different siding materials, you can make a confident decision. Remember to factor in long-term maintenance needs and environmental impact to ensure your choice is both practical and sustainable. With the information provided, you’re now well-prepared to embark on your siding project with confidence, transforming your home’s exterior into a reflection of your style and sound homeownership.
FAQ
What’s the average lifespan of different siding types?
Lifespans vary greatly. Wood siding can last 20-50 years with proper maintenance, vinyl 20-40 years, fiber cement 50+ years, and metal 40+ years.
Can I install siding myself?
While DIY is possible for some siding types (like vinyl), professional installation is often recommended, especially for complex projects or materials like fiber cement and metal. Improper installation can lead to costly repairs down the line.
How often should I clean my siding?
Regular cleaning, ideally once or twice a year, helps prevent dirt and debris buildup. The frequency might increase depending on your climate and the type of siding.
What are the signs I need siding repair?
Look for cracks, holes, loose or damaged panels, water stains, or signs of rotting wood. Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent more extensive and costly repairs later.
How much does professional siding installation typically cost?
Costs vary significantly based on location, material choice, house size, and labor rates. Get multiple quotes from reputable contractors to compare pricing.
Comments are closed.